
5 Essential Standards for Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The pharmaceutical industry encompasses every aspect of medications and drugs, meaning businesses in this industry develop, optimize, produce, and market medications for a wide range of medical conditions, from over-the-counter headache pills to advanced treatments for cancer and other diseases. It is an industry with global revenues of $1.2 trillion USD (IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science), truly impacting nearly every person on earth.
ASTM International’s committee on the manufacture of pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical products (E55) was created to address many facets of this expansive field. Formed in 2003, the group addresses issues related to “process control, design, and performance, as well as quality acceptance/assurance tests for the pharmaceutical manufacturing industry.” It works with drug and drug-equipment makers, government agencies, designers, professional societies, trade associations, financial organizations, and those in academia.
READ MORE: Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Gets Smart
Ferdinando Aspesi is a senior partner with Bridge Associates International, a manufacturing and operations consultancy serving this market. He chairs E55. He highlighted several standards as being the most important to the critical work of this committee:
1) Standard Guide for Specification, Design, and Verification of Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing Systems and Equipment (E2500)
“Under the guidelines of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, pharmaceutical manufacturing systems and equipment must meet certain requirements for design, installation, operation, and performance. Until publication of this guide in 2007, meeting these requirements was costly and time-consuming. With the guide, compliance now can be done at the supplier level, using their documentation as evidence that everything was built and functions as intended, eliminating the need for laborious re-testing at other stages in the process – and resulting in major savings for the pharmaceutical industry.”
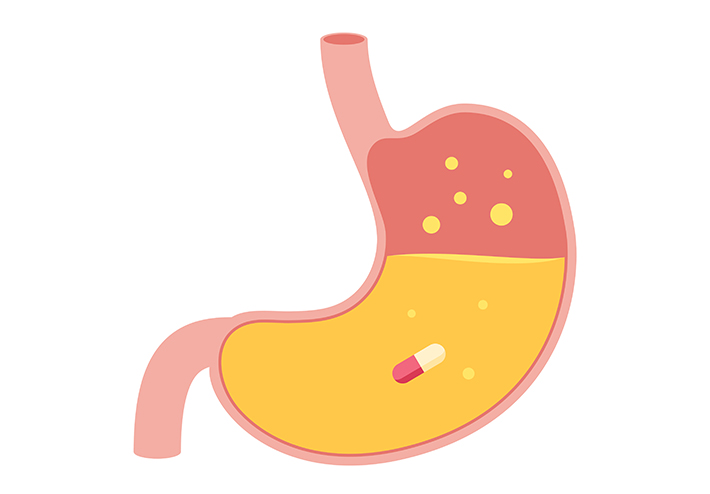
E2503 simulates the dissolving of a pill in the stomach.
2) Standard Practice for Qualification of Basket and Paddle Dissolution Apparatus (E2503)
“While not obvious from the title, this standard addresses the testing process for how quickly and effectively a drug tablet dissolves in a patient’s stomach. The process for doing that involves a basket and paddle apparatus that simulates that process of dissolution that previously required costly and time-consuming calibration before every test. By establishing a procedure for the mechanical calibration of these paddle and basket units, this standard allows manufacturers to confirm that their results are reproducible, eliminating the need to recalibrate the unit between each use. In addition to cost savings, this has also led to greater testing accuracy.”
3) Standard Practice for Pharmaceutical Process Design Utilizing Process Analytical Technology (E2474)
Process development and optimization for any new product both begin with process design, which is based on process analytical technology. This standard is focused on “practical implementation and experimental development of process understanding,” which is another way of saying it streamlines the manufacture of large quantities of pharmaceuticals. The standard brings together a number of different aspects including risk management, continuous improvement, intrinsic performance assessment, manufacturing strategy, data collection, and more. The process design integrates all of these elements in order to execute a strong, repeatable process for drug development and manufacturing.
4) Standard Guide for Application of Continuous Process Verification to Pharmaceutical and Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing (E2537)
“Continuous process verification offers an upgraded approach to process validation that saves both time and money by continuously monitoring the performance of a manufacturing process, evaluating performance and making adjustments on the fly if needed. In pharmaceutical manufacturing, which is regulated not only by the FDA in the U.S. but by similar government bodies all over the world, a science-based approach is needed to verify that a manufacturing process will consistently produce a product that meets its predetermined critical quality attributes, the type of cross-border production that this standard supports.

Rodent-derived cell cultures are covered by E2888.
5) Standard Practice for Process for Inactivation of Rodent Retrovirus by pH (E2888)
“Rodent-derived cell cultures are typically used in medical research to test the efficacy of drugs and treatments, but until the creation of this standard there was no accepted baseline for the process to deactivate retroviruses in these samples. E2888 assures inactivation of non-defective C-type retroviruses, keeping them out of the production stream of biopharmaceutical processes that use rodent-derived cell cultures.”
Tim Sprinkle is a freelance writer based in Colorado Springs, Colorado. He has written for Yahoo, The Street, and other websites.
 SN Home
SN Home Archive
Archive Advertisers
Advertisers Masthead
Masthead RateCard
RateCard Subscribe
Subscribe Email Editor
Email Editor