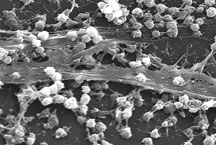
Biofilm
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency regulates pesticides under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide and Rodenticide Act. The EPA requires companies seeking to register public health pesticide products, including products designed to treat surfaces contaminated with biofilm, to ensure the effectiveness of their products before they are sold or distributed, and to provide that data to the agency. To ensure effectiveness, applicants are required to submit efficacy data to the EPA to demonstrate that, when used according to label directions, the product will be effective against microorganisms identified on the label.
ASTM Subcommittee E35.15 on Antimicrobial Agents is currently developing a proposed quantitative test method capable of reliably evaluating the efficacy of liquid disinfectants against biofilm: WK32449, Test Method for Testing Disinfectant Efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Grown in the CDC Biofilm Reactor Using the Single Tube Method.
The EPA's Office of Pesticide Programs Microbiology Laboratory Branch developed a protocol for evaluating the efficacy of liquid disinfectants against Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 15442 biofilm grown on borosilicate glass coupons in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention biofilm reactor according to ASTM E2562, Test Method for Quantification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Grown with High Shear and Continuous Flow Using CDC Biofilm Reactor. The OPP collaborated with the Montana State University Standardized Biofilm Methods Research Area at the Center for Biofilm Engineering for the purpose of assessing the performance and developing the method into the proposed WK32449.
WK32449 is the fifth biofilm method that E35.15 has developed. E35.15 is under the jurisdiction of ASTM International Committee E35 on Pesticides, Antimicrobials and Alternative Control Methods.
Biofilm grows in incredibly diverse environments. To accurately model these diverse conditions in the laboratory, a collection of methods needs to exist. The first three approved ASTM biofilm methods (E2196, Test Method for Quantification of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Grown with Shear and Continuous Flow Using a Rotating Disk Reactor; E2562; and E2647, Test Method for Quantification of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Grown Using a Drip Flow Biofilm Reactor with Low Shear and Continuous Flow) describe how to grow repeatable biofilm using three different biological continuous flow reactors (rotating disk reactor, CDC biofilm reactor and drip flow reactor) that model different fluid dynamics, from low shear to high shear.
The latest approved biofilm method, E2799, Test Method for Testing Disinfectant Efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Using the MBEC Assay, first grows a repeatable biofilm in a batch reactor using the MBEC device, then tests the efficacy of liquid disinfectants against the resulting biofilm. The goal of E35.15 is to develop a collection of methods for growing, treating, sampling and analyzing biofilm bacteria that will enable academic, regulatory and industrial laboratories to have options for choosing the best method relevant for their biofilm research needs.
To purchase ASTM standards, visit www.astm.org and search by the standard designation number, or contact ASTM Customer Relations (phone: 610-832-9585).
CONTACT Technical Information: Darla Goeres, Center for Biofilm Engineering, Montana State University • Bozeman, Mont. • Phone: 606-994-2440 • Email: darla_g@erc.montana.edu O ASTM Staff: Jennifer Rodgers • Phone: 610-832-9694 • Email: jrodgers@astm.org O Upcoming Meeting: Oct. 31-Nov. 3 • October Committee Week • Tampa, Fla.
 SN Home
SN Home Archive
Archive Advertisers
Advertisers Masthead
Masthead RateCard
RateCard Subscribe
Subscribe Email Editor
Email Editor