Microindentation Hardness
A recent revision to ASTM International standard E384, Test Method for Knoop and Vickers Hardness of Materials, expands the range of its coverage. The standard is under the jurisdiction of Subcommittee E04.05 on Microindentation Hardness Testing, part of ASTM International Committee E04 on Metallography.The revision included the incorporation of E92, Test Method for Vickers Hardness of Metallic Materials, into E384. E92 is under the jurisdiction of ASTM International Committee E28 on Mechanical Testing.
According to Edward Tobolski, chairman of Committee E28 and chairman of Subcommittee E04.05, in the past, hardness testers normally were designed to perform either micro (E384) or macro (E92) hardness tests. The main difference between the two is the test forces used; micro is 1 kg and lower, and macro is 1 kg and higher. However, newer testing equipment frequently has the capability of covering both force ranges.
"Subcommittee E28.06 on Indentation Hardness Testing was in the process of revising E92 to lower the range to 200 g, which would put it well into the traditionally micro range," says Tobolski. "If that was done, users would have to get calibration certificates for both standards at the same test forces."Instead, it was decided that E384 would be expanded to include the requirements defined in E92. In doing so, E04.05 was careful to revise E384 so that older testers that are E384 and E92 compliant will still comply with the revised E384. E92 is to be balloted for withdrawal.
The main users of E384 would be anyone hardening a material through a heat treatment process. E384 is frequently the best method to verify that heat treatment is working properly.
Tobolski notes that E04.05 would encourage users of E384 to participate in its ongoing development. "The next revision will address defining the optical systems resolution," says Tobolski. "Anyone with a knowledge of optics and how they relate to hardness testing would be welcome to help revise E384."To purchase ASTM International standards, visit www.astm.org and search by the standard designation number, or contact ASTM Customer Relations (phone: 610-832-9585).
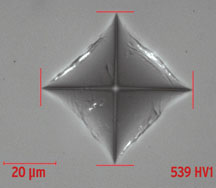
CONTACT Technical Information: Edward Tobolski • Wrentham, Mass. • Phone: 508-384-6341 • E-mail: tobolsed@verizon.net O ASTM Staff: Kathleen McClung • Phone: 610-832-9717 • E-mail: kmcclung@astm.org O Upcoming Meeting: May 17-18 • May Committee Week • St. Louis, Mo.Vickers indent in ceramic.
 SN Home
SN Home Archive
Archive Advertisers
Advertisers Masthead
Masthead RateCard
RateCard Subscribe
Subscribe Email Editor
Email Editor